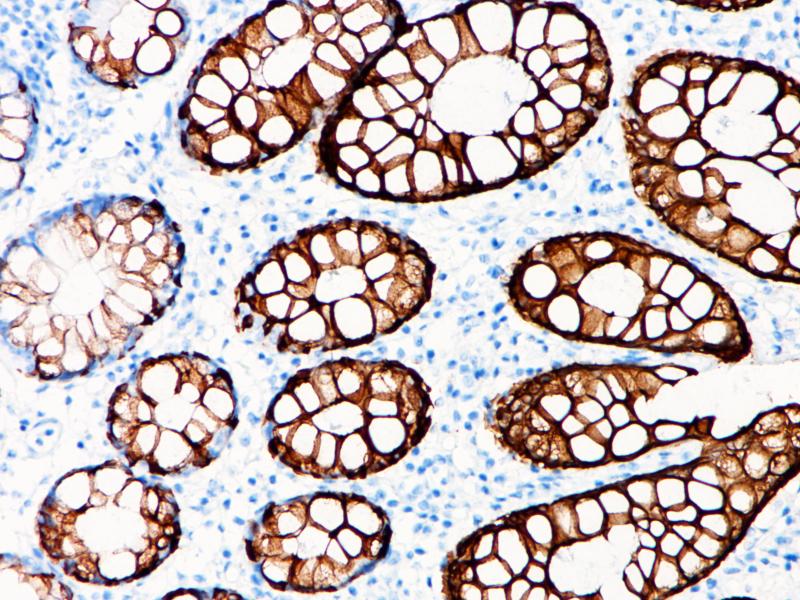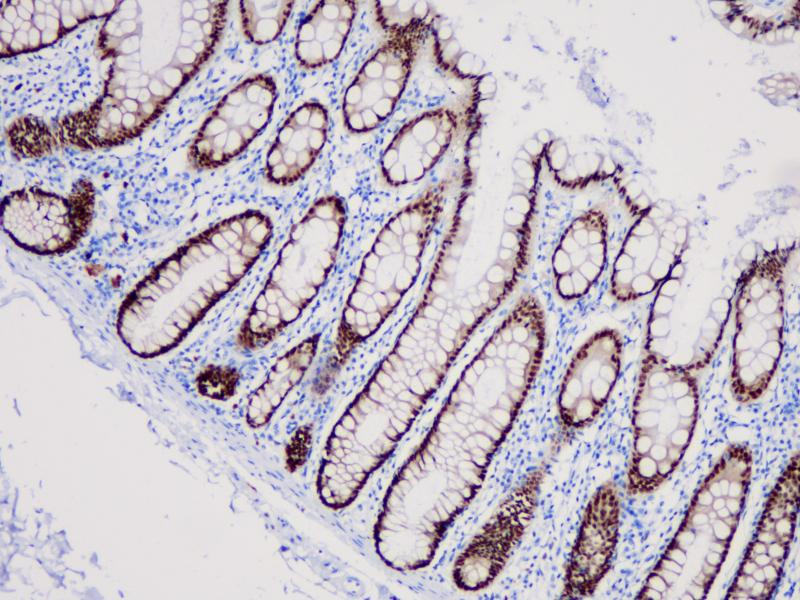
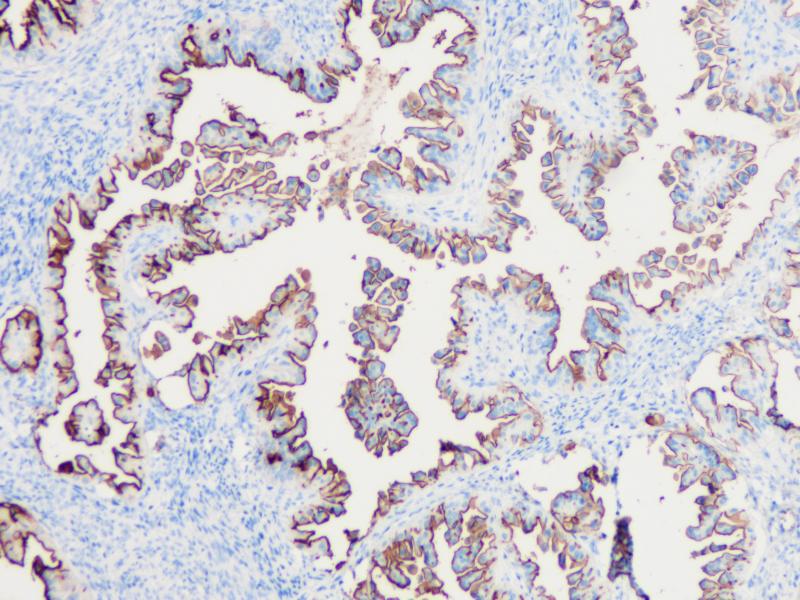
Ovarian cancer
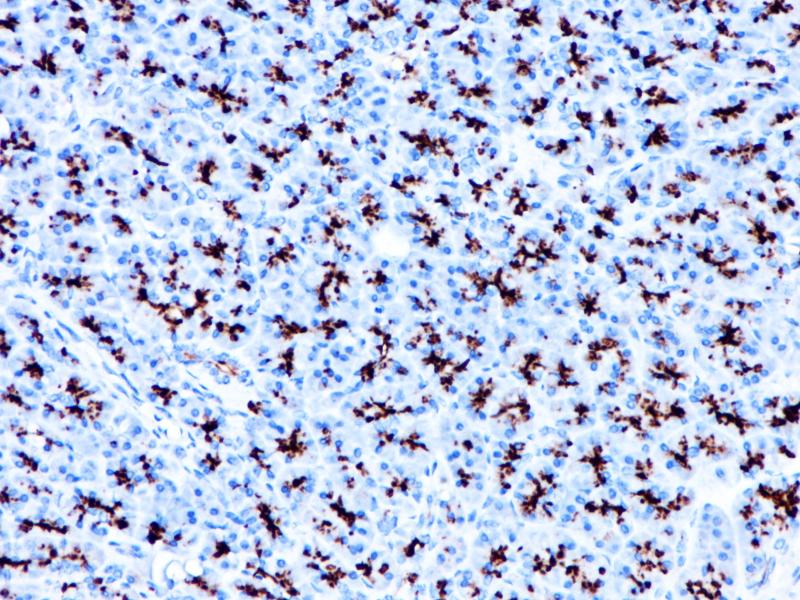
Pancreas
MUC1 Recombinant Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody
MUC1 (Mucin 1) is a transmembrane glycoprotein that protects epithelial cells from injury caused by external stimuli. In addition to this role, MUC1 is involved in cell-cell adhesion, proliferation, motility, invasion and survival. In epithelial cells, MUC1 expression is regulated by binding of TNFα to TNFR1 and activation of the NFκB pathway.
MUC1 is present in a variety of glandular (secretory) epithelia such as breast, eccrine and apocrine glands, and pancreas, whereas little or no MUC1 is expressed in the gastrointestinal epithelium, endocervical epithelium, and prostate glands. The immunoreactivity is usually limited to apical cell membranes, but a staining of the Golgi zone may also be seen. MUC1 can be demonstrated in most types of adenocarcinomas derived from secretory epithelia. In well-differentiated carcinomas, the staining is mostly limited to (apical) cell membranes while in the less differentiated carcinomas, a cytoplasmic staining is seen with loss of staining polarity in the membranes.
MUC1 was used to recognize epithelial differentiation when cytokeratin was difficult to visualize. In the classification of haematolymphoid neoplasms, a positive MUC1 reaction may be an aid in the identification of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, plasma cell neoplasms and nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin's lymphoma.
MUC1 is present in a variety of glandular (secretory) epithelia such as breast, eccrine and apocrine glands, and pancreas, whereas little or no MUC1 is expressed in the gastrointestinal epithelium, endocervical epithelium, and prostate glands. The immunoreactivity is usually limited to apical cell membranes, but a staining of the Golgi zone may also be seen. MUC1 can be demonstrated in most types of adenocarcinomas derived from secretory epithelia. In well-differentiated carcinomas, the staining is mostly limited to (apical) cell membranes while in the less differentiated carcinomas, a cytoplasmic staining is seen with loss of staining polarity in the membranes.
MUC1 was used to recognize epithelial differentiation when cytokeratin was difficult to visualize. In the classification of haematolymphoid neoplasms, a positive MUC1 reaction may be an aid in the identification of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, plasma cell neoplasms and nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin's lymphoma.
Specifications
- Catalog No.
- BX50029
- Clone No.
- BP6034
- Application
- IHC-P
- Subcellular location
- Membrane/Cytoplasm
- Control
- Ovarian cancer
- Recommended method
- HIER
- Volume
- 100μl/vial, 1ml/vial
- Dilution
- 1:100-1:200
- Immunogen
- Synthetic peptide corresponding to MUC1 residues within aa1155-1255 of MUC1 was used as an immunogen.
Reference
1.Croce MV, et.al, J Histochem Cytochem. 2003 Jun;51(6):781-8.
2.Nakamori S, et.al, Gastroenterology. 1994 Feb;106(2):353-61.
Support Documents
Order
- E-mail : sales@biolynx.cn