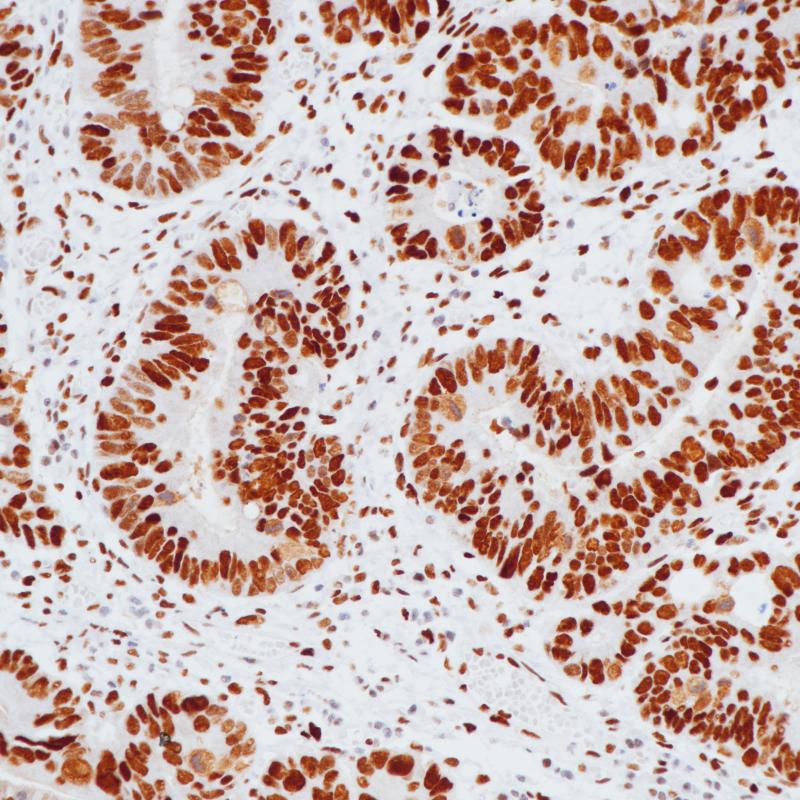
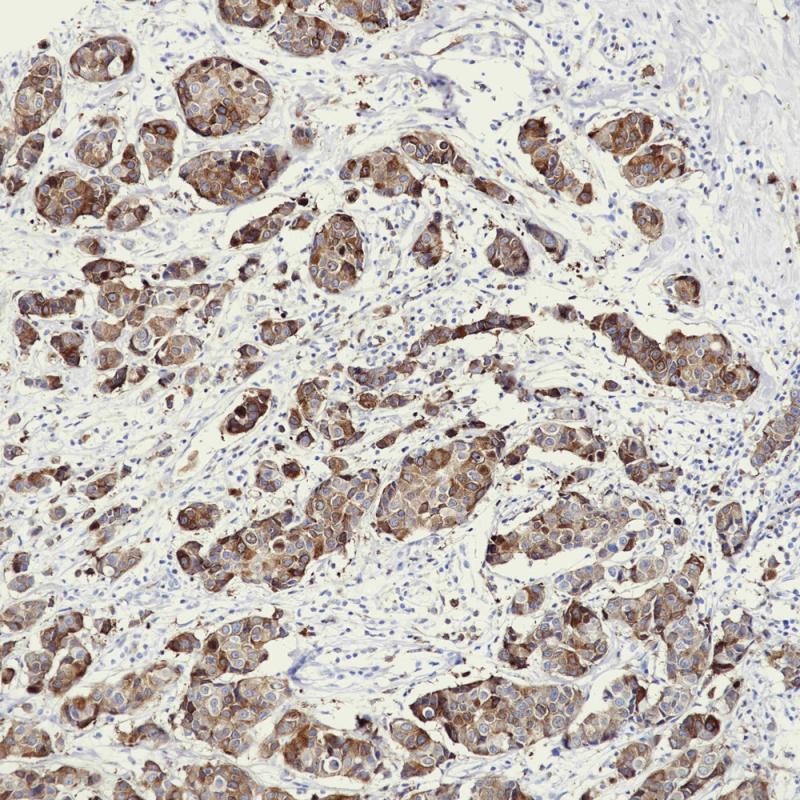
Breast Carcinoma
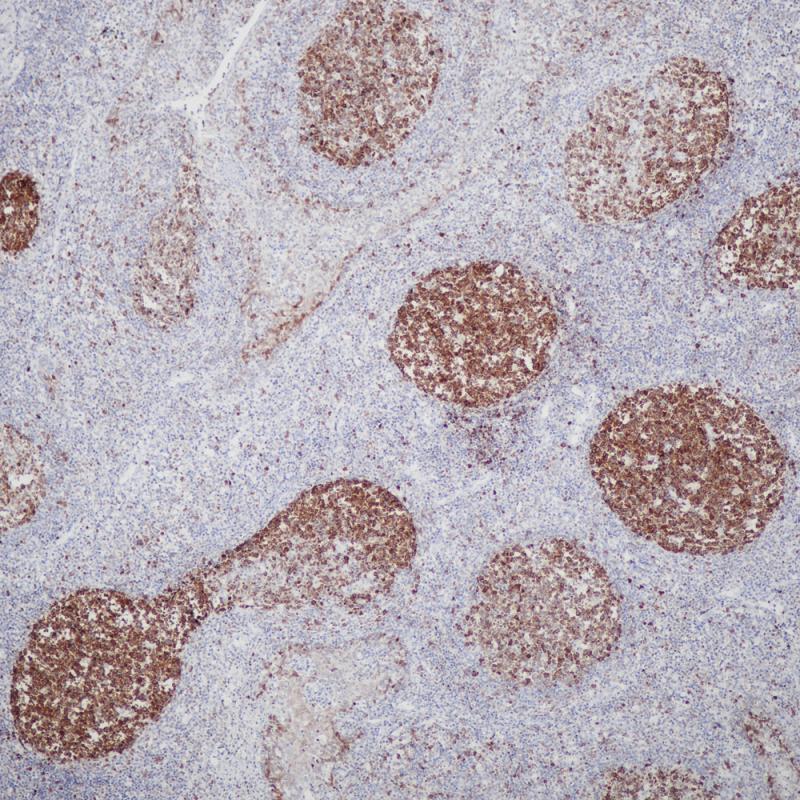
Tonsil
RRM1 Recombinant Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody
Ribonucleotide reductase M1 polypeptide (RRM1) is one of two non-identical subunits for ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase, an enzyme which catalyzes the biosynthesis of deoxyribonucleotides from the corresponding ribonucleotides. It provides the precursors necessary for DNA synthesis. RRM1 is present throughout the cell division cycle but downregulated in quiescent cells. RRM1 is involved in carcinogenesis, tumor progression, and the response of non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) to chemotherapy.
Specifications
- Catalog No.
- BX50118
- Clone No.
- BP6122
- Application
- IHC-P
- Subcellular location
- Breast Carcinoma
- Control
- Cytoplasmic
- Recommended method
- HIER
- Volume
- 100μl/vial, 1ml/vial
- Dilution
- 1:100-1:200
- Immunogen
- Synthetic peptide corresponding to residues within aa700-800 of Human RRM1 was used as an immunogen.
Reference
1.Wang, Q, et al. PLoS ONE. 2013 Jul;8(7):1-12.
2.Nordlund P, et al. Annu Rev Biochem. 2006; 75:681–706.
Support Documents
Order
- E-mail : sales@biolynx.cn